Rare Diseases of Endocrine System
Gigantism
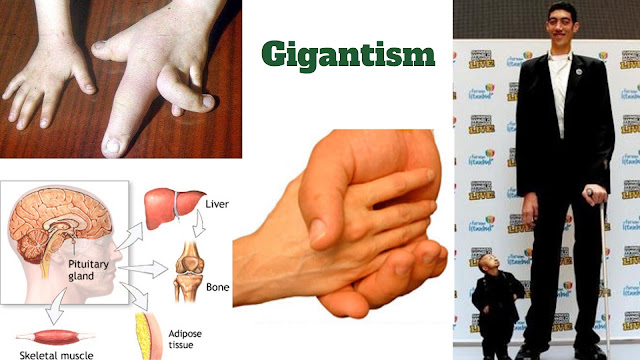
Gigantism also called gigantism obtained from a Greek word gigas, is a Rare Endocrine Diseases characterized by excessive growth hormone which accelerates the growth of muscle, bones and connective tissue in childhood or youth before the end of puberty. It is always the consequence of a growth hormone secreting pituitary tumour. When left untreated or uncontrolled, some individuals suffering from gigantism have grown in excess of eight feet (2.4 m) tall. The most well-known example is that of Robert Wadlow, the tallest person in history.
Cause
Most common reason of gigantism is Pituitary gland tumor. The pea sized pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain; it makes hormones that control body temperature, metabolism growth, sexual development and urine production.
Some other cause of gigantism is:
· McCune-Albright disease is a disorder that causes unusual growth of bone tissues, gland irregularities and patches of light-brown skin.
· Carney complex is a hereditary condition which cancerous or non-cancerous endocrine tumors and spots of darker skin.
· Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 is also a hereditary condition which causes tumours in the pancreas, parathyroid glands and pituitary gland.
· Neurofibromatosis is a hereditary disease that causes tumors in the nervous system.
Signs
The symptoms may depend on the size of the pituitary gland tumor. As the tumor grows, it might press on nerves in the brain. Various people experience headaches, vision problems or nausea from tumors in this area. Other symptoms include,
· Delayed puberty
· Increased sweating
· Gaps between teeth
· Deafness
· Insomnia and other sleep disorders.
· Young girls will have release of breast milk & irregular periods
· Thickening of the facial features(as the tumor grows it may press on nerves in the brain)
Diagnosis
· If gigantism is suspected, the diagnosis is usually confirmed by taking blood test in-order to measure the levels of growth hormone and also insulin-like growth factor 1 is secreted into the blood primarily by the liver.
· An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is also performed. This includes drinking a glucose solution and then having blood samples taken periodically in order to evaluate the growth of hormone level. If the person suffers, the GH level does not suppress to low levels than in a normal population.
· If that blood tests specify gigantism, then you have to perform another test like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scan of that gland in order to assess the size and also the position of the tumor.
Treatment
· Surgery to remove any possible tumors on the pituitary gland, if the tumor has well defined borders.
· Drug therapy is then used to control the production of more human until the body itself is able to control it.
· In case when surgery is not an option, medication is the treatment of choice;
1. Somatostatin analogs and dopamine agonists- reduce GH release
2. Pegvisomant blocks effect of GH.


Comments
Post a Comment